Poster presented on Asilomar 2019

Authors: Md Moin Uddin Atique, Joseph T. Francis
Abstract for SFN 2019:
Sensorimotor cortices play an important role during movement and action observation. Previous work has introduced the fact that reward level can modulate activity in S1 (McNiel et al 2016). In this study, we show that force related activity in S1 is also modulated by the cued level of possible reward. We analyzed data from two monkeys, one male (Macaca radiata, Monkey S) and one female (Macaca Mulatta, Monkey P). Trials consisted of a psychophysical task where the monkey had to apply an appropriate amount of grip force to a force transducer to enable a simulated robotic manipulator to grasp and transport an object to a targeted location. For each of these monkeys, we used two different blocks of manual trials. One block consisted of trials where the monkeys were given a cue for the level of reward while the other block was uncued. We used the spiking activity of units from S1 for our analysis. We measured the significance (F-test, p-value < 0.05) between the spike rate of the units and applied grip force. Additionally, a separate analysis was performed to calculate the significance (t-test, a p-value< 0.05) for the reward level using the post reward spiking activity (500ms for each trial). The units that are common to both force and reward significance tests were collected. For Monkey S we have found 53 units that are significant for both force and reward and for monkey P the unit number was 22.


The raster plots during the cue presentation and reward delivery periods showed the difference in activities of the same unit between rewarding and non-rewarding trials, especially for the post cue and post reward time. The spiking activity of neurons during the grasping period represents a variation similar to the applied force. We used Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) on spike rate to predict force from manual cued and uncued blocks. The correlation coefficient (R-square) between the predicted force and the actual applied force for Monkey S was 0.86 and 0.83 and for Monkey P was 0.83 and 0.82. That represents, the force can be decoded from the neural activity of S1 units.

We computed the linear tuning curves for the force during rewarding and non-rewarding trials and measured if they are significantly different for each individual units (F-test, p-value < 0.05). For Monkey S, in the cued manual block, there were 21 units that showed a significant difference between tuning curves of rewarding and non-rewarding trials whereas the number of significant units were 30 for Monkey P. The results we have presented here demonstrate that units from S1 have a representation of grip force and this representation can be modulated by the reward expectation.
This project is an update work of the project previously posted. This version is successfully tested on amputee person.
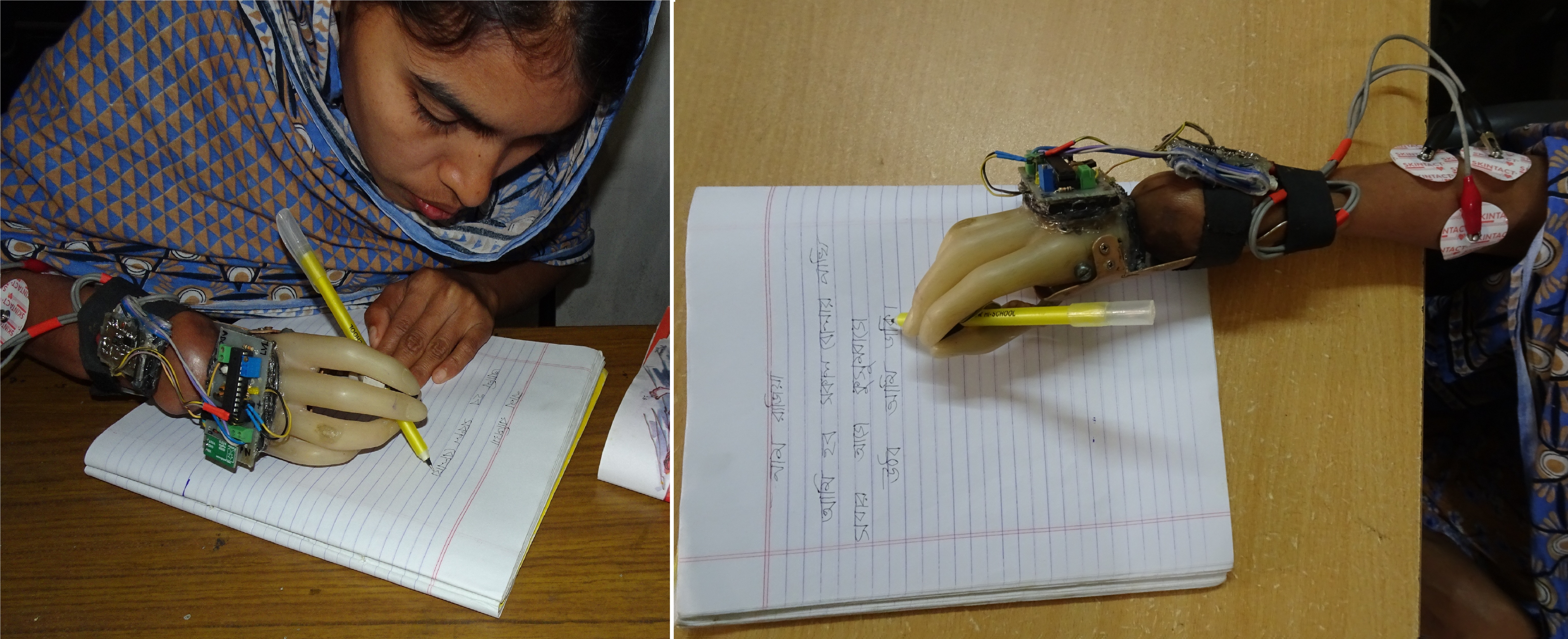
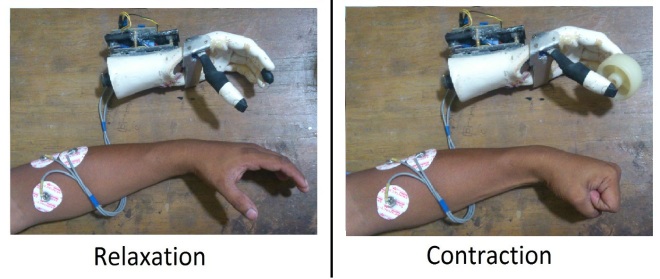
The goal of this work was to develop a cost-effective myoelectric prosthetic hand for wrist amputees. The prosthetic hand was improvised from the hand of a mannequin (dolls to display dresses in shops) to give a realistic appearance. The thumb was cut out and was fitted back with a spring mechanism and a DC gear motor and could be rotated around a fixed axis so that it closed onto the index finger and the middle finger for a gripping action. The motor was controlled using muscles electrical potentials (Electromyogram-EMG), which generated by contracting specific muscles through thought processes of the brain. Instead of manipulating all the fingers, which would be complex, expensive and demanding on battery power, this prosthetic hand was designed to have only a rotating thumb, the rest of the fingers being fixed. This thumb control provides a great deal of functionality to the user giving a cost effective solution.
Surface electrodes were used to pick up the EMG signals. A bioelectric amplifier was designed and developed to detect and amplify EMG signals which was then fed to a microcontroller having a built in analogue to digital converter. Necesary software was developed to detect the presence of the amplified EMG signal and to control DC motor through a motor drive circuitry. The thumb of the developed unit responded to contraction of the arm muscles as desired. This cost effective semi-functional prosthetic hand, controlled by EMG signals will be a solution for many in need.
Publication:
Electrooculography (EOG) is the electrical activity due to eyeballs’ movement, recorded from the different points of face. Human-Computer Interface (HCI) application based on EOG could be very helpful for the patients suffering from neural diseases like Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) or paralysis. In the present work two EOG amplifiers have been used to detect five different movement of the eyes of a user.
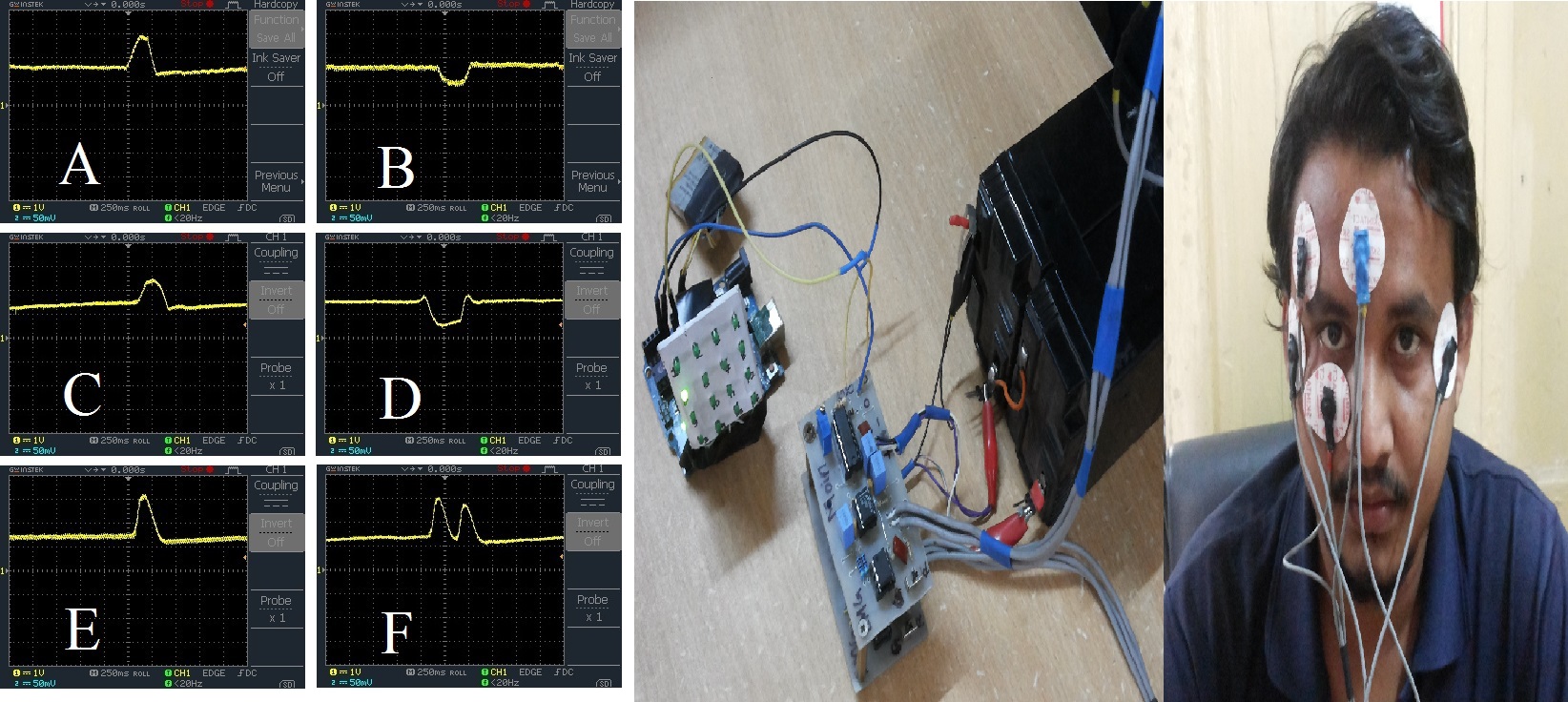
Through a microcontroller interface these five commands have been used by a subject to choose and turn on/off any of 16 LEDs arranged in a matrix of (4×4) at his/her will. Right, Left, Up and Down movement of the eye shifts the position of the lit LED while a Blinking action of the eye activates an action on that chosen LED. In future this technique can be used in HCI based applications.
Prosthesis for amputee personals may help them to lead a normal life. Limb prosthesis is a very ancient and important research topic. The goal of this experiment was to develop a cost-effective myoelectric prosthetic hand for wrist amputees in which the wearer will be able to control the thumb through voluntary EMG signals- generated by the brain. Instead of manipulating all the fingers, which would be complex, expensive and demanding on battery power, this prosthetic hand is designed to have only a moving thumb, the rest are fixed. This thumb control provides a great deal of functionality to the user giving a cost effective solution. The prosthetic hand was improvised from the hand of a mannequin (dolls for showing dresses) in which the thumb was cut out from the rest and was fitted back using a geared servo motor. The thumb could be rotated around a fixed axis so that it closed onto the forefinger and the middle finger for a gripping action.

This controlling mechanism is performed using EMG signals from the extensor or flexor muscle group of the forearm. Surface electrodes were used as the transducers to detect the EMG signals. A bio-amplifier was designed to detect and amplify EMG signals. A microcontroller sensed the presence of the amplified EMG signal and controlled the servo motor depending on its availability. Since voluntary EMG signals are due to the effect of signals from the brain, the prosthetic hand is effectively controlled by the thought of the user. The magnitudes of the EMG signal may vary person to person, so an adjustment unit was added.
Hand prosthesis is available from some groups around the world, are extremely expensive and beyond affordability of the common people. A cost effective low bud- get semi-functional prosthetic hand, controlled by EMG signals will be a solution for many in need.
This thesis project was funded by the Information and Communication Technology Ministry, Bangladesh.
Publication:
Walking robot is always of interest among the researchers. Mimicking the walking pattern of different animals is fascinating and challenging. A quadruped robot has four legs and walks similar to a spider. Autonomous feature to perform some given tasks is important and this requires some sensors like distance measurement, accelerometer, gyro meter, camera, GPS etc. Moreover, because of the widespread availability of Android based smart phones, it will be better if the robot could be controlled from the smart phones using blue-tooth technology.
In my project I have designed and constructed a 2DOF Quadruped robot. The structure is designed and created from aluminum sheets. Arduino Uno microcontroller board, 9G servo motor, Ultrasound sensor, HC-05 Bluetooth module, Accelerometer, Gyro-meter are used on the robot. An android application is developed which is able to control the robot using Bluetooth.
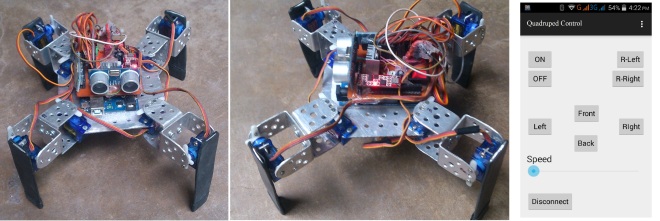
The robot currently have 6 different movements including, front, back, left, right walking and clockwise and anti-clockwise rotation. The robot uses the ultrasound sensor to detect the distance and if some obstacles appear, it will stop moving to that direction.
CNC (computer numeric control) machines are very useful for industrial purpose as well as laboratory research uses. Since they automatically perform the tasks from a given design like making parts, PCB boards, grooving, cutting and so on, a good amount of time could be saved if they are used. For laboratory or home use commercially available CNC machines are cost prohibitive. A low budget CNC machine would be handy for the researchers.

The CNC, designed in this project is mostly made out of parts taken from old printers and scanners. The circuits are designed and fabricated to control the stepper motors, communicate between PCs and they also supply power to the device. Software and algorithm is developed to control the machine as simply as possible. The Arduino Mega 2560 microcontroller board is used as the controller. Processing language is used to create the software to control the machine from PC.
Switches are used to detect initial position for three axes. The machine can be controlled through a controller board and also from PC software. This machine can cut circles or box shapes of given dimension on a given position of a wood board or PCB board. G-code conversion software will be developed to cut any desired pattern from the available designing software and then it will be able to create circuits from a single sided PCB boards.
A uniform volume conductor has symmetrical distribution of electrical impedance. Electrical impedance will change in the presence of a substance (conductor or insulator or any biological tissue) whose dielectric properties differ from that uniform volume conductor. This impedance change could be measured by surface electrodes. Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) is a technique by which impedance measurements on surface of an object are reconstructed into impedance images. It is fast, inexpensive and non-invasive but has relatively low spatial resolution. This paper describes a simple but effective method of detection and localization of objects within a volume conductor using electrical impedance measurements. Sixteen electrodes were placed equidistantly on the surface of a cylindrical tank filled with saline and electrical transfer impedances from 6 pair of electrodes were measured. Similar impedance profiles were also measured by placing in homogeneity (iron rod and glass sphere) at an arbitrary position. Absolute impedance variation from the uniform volume conductor impedance for both objects is calculated and plotted. For both cases, the absolute impedance variation showed maximum value for the electrode near the object which confirms that detection and localization of objects within volume conductor is possible by the proposed method. This project is published In Proceedings of International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT-2014) and is available on the IEEE Xplore
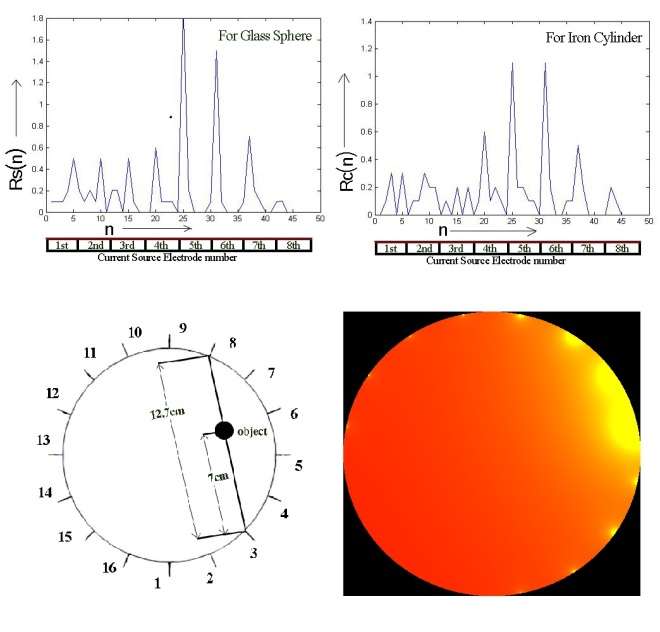
A simple attempt to create an EIT image is made with the recorded data. The algorithm is not well constructed yet and is still under development but at present it constructs images from which an approximate location of the object, placed in homogeneous volume conductor can be deduced.
Robotic manipulators are very common for different robotic applications. We designed and created a 3DOF robotic leg shaped structure. Then we deduced the Kinematics and Inverse Kinematics solution through Denavit-Hartenberg Convention and with that solution, simulation software is designed to predict the movement and also to control the robotic structure. This simulation software gives predicted results for the robotic structure.
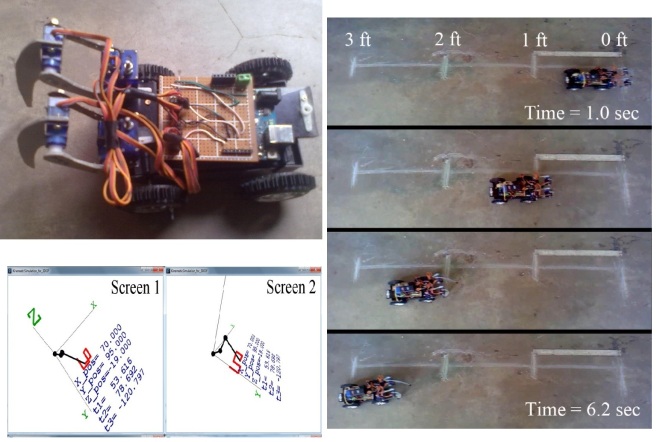
After that we attached two of the robotic legs with a small car and moved the car by pushing through them. With the robotic leg the car moved at about 0.48 feet/second velocity. This project is published In Proceedings of International Conference on Informatics, Electronics & Vision (ICIEV-2014) and is available on the IEEE Xplore
Anemia is a very common disease. Around 30-40% of the people are affected by Anemia. It occurs when the percentage of hemoglobin on a person’s blood reduces below a certain level. Sometimes in emergency, the percentage of hemoglobin is necessary to know. If a software can predict the percentage of hemoglobin on blood and detect anemia in seconds that will be very useful. Doctors can detect Anemia from patients’ inner side of the lower eyelid, but they cannot determine the percentage of hemoglobin without blood testing. It expresses that the RGB color of inner side of the lower eyelid’s image is related to the percentage of hemoglobin. The goal of this project is to find out a relationship between them. Images of eyelid from seven individual have been collected along with their blood test for determining the percentage of hemoglobin. A software is developed to measure the average Red color value from the eyelid image. This average value is plotted with the percentage of hemoglobin to observe the variation.
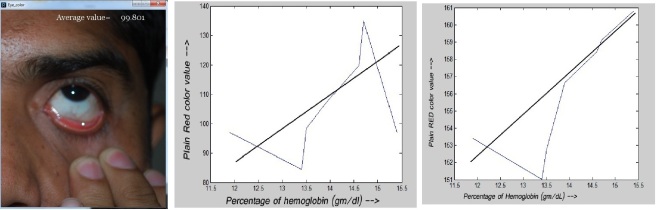
Although the graph was jittery a trend of proportional relation between them is observed. This jittery on the graph may occurred because of the photo collection procedure was not ideal. A better studio environment may reduce this problem. Also the increased number of sample will be helpful for such study.
This project is the idea of Dr. Khondkar Siddique-e-Rabbani. I have submitted this as my undergraduate project with Rafiqul Islam Sarker, department of EEE, University of Dhaka. I have received a lots of help from the Department of Biomedical Physics department, University of Dhaka.